拓扑排序(一)
post by:追风剑情 2015-12-6 19:34
拓扑排序与AOV、AOE网主要用来处理工程管理的。
在图论中,一个有向无环图的所有顶点可以排成一个线性序列,当这个线性序列满足以下条件时,称该序列为一个满足图的拓扑次序(topological order)的序列。
(1)图中的每个顶点在序列中只出现一次;
(2)对于图中任意一条有向边(u, v),在该序列中顶点u一定位于顶点v之前。
这样的序列也被称为拓扑序列,对有向图的所有顶点排序,获得拓扑序列的过程就是有向图的拓扑排序(topological sorting)。拓扑排序并不仅仅用于有向图,它是一种利用数据元素中某个属性的偏序关系得到数据元素的全排序序列的方法。
拓扑排序的基本过程:
(1) 从有向图中选择一个没有前驱(入度为0)的顶点,输出这个顶点。
(2) 从有向图中删除该顶点,同时删除由该顶点发出的所有有向边。
重复上述步骤(1)和(2),直到图中不再有入度为0的顶点为止。此时,如果所有的顶点都已经输出,则顺序输出的顶点序列就是一个拓扑序列,如果图中还有未输出的顶点,但是入度都不为0,则说明有向图中存在环路,不能进行拓扑排序。
拓扑排序的现实意义在于,如果按照拓扑序列中的顶点次序安排活动,则在每一项活动开始的时候,能够保证它所依赖的所有前驱活动都已经完成,从而使得整个工程可以顺利进行,不出现冲突。需要注意的是,对于一个有向无环图来说,有时候不只一个有序的拓扑序列。
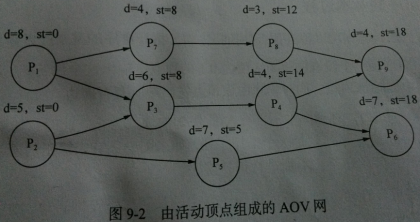
示例
工程活动关系图
代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace TopSortTest
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//测试工程活动拓扑排序
Activity activity = new Activity();
activity.InitGraph();
activity.TopSort();
Console.Read();
}
}
// 活动
class Activity
{
Graph graph;
PriorityQueue queue;
// 初始化工程活动
public void InitGraph()
{
queue = new PriorityQueue();
//根据工程活动关系表构造有向图 (采用AOV网 + 邻接表)
graph = new Graph();
graph.vertexs = new VertexNode[9];
int[] days = new int[] { 8, 5, 6, 4, 7, 7, 4, 3, 4 };
int[] inCount = new int[] { 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2 };
List<int[]> adjacentNode = new List<int[]>();
adjacentNode.Add( new int[] { 6, 2 } );
adjacentNode.Add( new int[] { 4, 2 } );
adjacentNode.Add( new int[] { 3 } );
adjacentNode.Add( new int[] { 5, 8 } );
adjacentNode.Add( new int[] { 5 } );
adjacentNode.Add( null );
adjacentNode.Add( new int[] { 7 } );
adjacentNode.Add( new int[] { 8 } );
adjacentNode.Add( null );
for (int i = 0; i < graph.vertexs.Length; i++)
{
VertexNode v = new VertexNode();
graph.vertexs[i] = v;
v.name = "P" + i;
v.days = days[i];
v.inCount = inCount[i];
v.adjacentNode = adjacentNode[i];
//活动最早开始时间的自动计算算法以后再讲,这里暂时随便赋个值。
v.sTime = new Random().Next(100);
}
}
// 对活动有向图进行拓扑排序
public bool TopSort()
{
List<VertexNode> sortedNode = new List<VertexNode>();
//所有入度为0的活动进队列
for (int i = 0; i < graph.vertexs.Length; i++)
{
if (graph.vertexs[i].inCount == 0)
queue.Enqueue(graph.vertexs[i]);
}
while (queue.Count > 0)
{
VertexNode node = queue.Dequeue();
sortedNode.Add(node);
if (null == node.adjacentNode)
continue;
//遍历节点node的所有邻接点,将表示有向边的inCount值减1
for (int j = 0; j < node.adjacentNode.Length; j++)
{
int adjNode = node.adjacentNode[j];
graph.vertexs[adjNode].inCount--;
//如果inCount值为0,则该节点入队列
if (graph.vertexs[adjNode].inCount == 0)
queue.Enqueue(graph.vertexs[adjNode]);
}
}
//如果有向图存在环路
if (sortedNode.Count != graph.vertexs.Length)
{
Console.WriteLine("有向图存在环路,活动无法顺利完成。");
return false;
}
//输出
Console.Write("拓扑排序: ");
for (int i = 0; i < sortedNode.Count; i++)
{
Console.Write(sortedNode[i].name + " ");
}
return true;
}
}
// 活动顶点数据结构
class VertexNode
{
public string name;//活动名称
public int days; //完成活动所需时间
public int sTime; //活动最早开始时间
public int inCount;//活动的前驱结点个数
public int[] adjacentNode;//相邻活动列表(节点索引)
}
// 活动图
class Graph
{
public VertexNode[] vertexs;//图的顶点列表
}
// 优先级队列
class PriorityQueue
{
private List<VertexNode> list = new List<VertexNode>();
public int Count
{
get
{
return list.Count;
}
}
public void Enqueue(VertexNode node)
{
Console.WriteLine("进队列: "+node.name);
list.Add(node);
list.Sort(Comparison);
}
public VertexNode Dequeue()
{
VertexNode node = null;
if (list.Count > 0)
{
node = list[0];
list.RemoveAt(0);
}
return node;
}
//按活动最早开始时间排序
int Comparison(VertexNode a, VertexNode b)
{
if (a.sTime > b.sTime)
return 1;
else if (a.sTime == b.sTime)
return 0;
return -1;
}
}
}
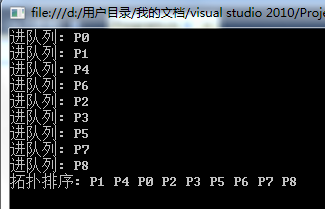
运行结果:
评论:
发表评论: