用二进制I/O进行随机访问
post by:追风剑情 2020-4-7 10:15
示例:用二进制I/O进行随机访问
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define ARSIZE 1000
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
double numbers[ARSIZE];
double value;
const char * file = "numbers.dat";
int i;
long pos;
FILE *iofile;
//创建一组double类型的值
for (i = 0; i < ARSIZE; i++)
numbers[i] = 100.0 * i + 1.0 / (i + 1);
//尝试打开文件
//注意:对于UNIX和Linux文本模式和二进制模式完全相同
if ((iofile = fopen(file, "wb")) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not open %s for output.\n", file);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//以二进制格式把数组写入文件
fwrite(numbers, sizeof(double), ARSIZE, iofile);
fclose(iofile);
if ((iofile = fopen(file, "rb")) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Could not open %s for random access.\n", file);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//从文件中读取选定的内容
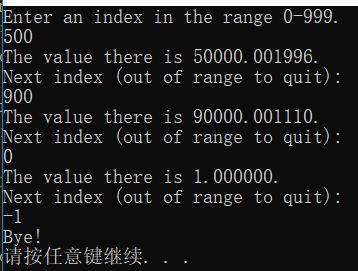
printf("Enter an index in the range 0-%d.\n", ARSIZE - 1);
while (scanf("%d", &i) == 1 && i >= 0 && i < ARSIZE)
{
pos = (long)i * sizeof(double); //计算偏移量
fseek(iofile, pos, SEEK_SET); //定位到此处
fread(&value, sizeof(double), 1, iofile);
printf("The value there is %f.\n", value);
printf("Next index (out of range to quit):\n");
}
//完成
fclose(iofile);
puts("Bye!");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行测试
评论:
发表评论: