随机数函数和静态变量
post by:追风剑情 2019-12-10 19:35
示例
s_and_r.c文件
//next是具有内部链接的文件作用域静态变量
//其他文件中的函数无法访问next
static unsigned long int next = 1; /* 种子 */
//采用ANSI C可移值的标准算法
int rand1(void)
{
/*生成伪随机数的魔术公式*/
next = next * 1103515245 + 12345;
return (unsigned int)(next / 65536) % 32768;
}
void srand1(unsigned int seed)
{
next = seed;
}
Main.c文件
//Visual Studio中加上这句才可以使用scanf()
//否则只能使用scanf_s()
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
//malloc()、free()
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
//函数的定义在另一个.c文件时,用extern关键字声明。
extern void srand1(unsigned int x);
extern int rand1(void);
//argc: 参数个数 argv[]: 参数数组
//int main(int argc, char **argv)
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int count;
unsigned seed;
printf("Please enter your choice for seed.\n");
while (scanf("%u", &seed) == 1)
{
srand1(seed); /* 重置种子 */
for (count = 0; count < 5; count++)
printf("%d\n", rand1());
printf("Please enter next seed (q to quit):\n");
}
printf("Done\n");
//也可以用系统时间作为随机种子
/*
time()返回值的类型名是time_t,具体类型与系统有关。
一般而言,time()接受的参数是一个time_t类型对象的地址,
而时间值就储存在传入的地址上。当然,也可以传入空指针(0)作为参数,
这种情况下,只能通过返回值机制来提供值。
*/
srand1((unsigned int) time(0));
for (count = 0; count < 5; count++)
printf("%d\n", rand1());
system("pause");
return 0;
}
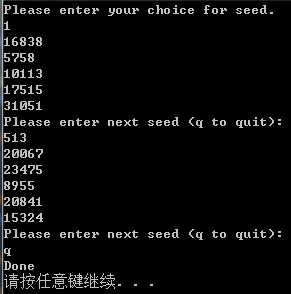
运行测试
评论:
发表评论: