单字符I/O: getchar()和putchar()
post by:追风剑情 2019-9-5 21:27
//Visual Studio中加上这句才可以使用scanf()
//否则只能使用scanf_s()
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// 验证输入是一个整数
long get_long(void);
// 验证范围的上下限是否有效
bool bad_limits(long begin, long end, long low, long high);
// 计算a~b之间的整数平方和
double sum_squares(long a, long b);
//argc: 参数个数 argv[]: 参数数组
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
const long MIN = -10000000L; // 范围的下限
const long MAX = +10000000L; // 范围的上限
long start; // 用户指定的范围最小值
long stop; // 用户指定的范围最大值
double answer;
printf("This program computes the sum of the squares of "
"integers in a range.\nThe lower bound should not "
"be less than -10000000 and \nthe upper bound "
"should not be more than +10000000.\nEnter the "
"limits (enter 0 for both limits to quit):\n"
"lower limit: ");
start = get_long();
printf("upper limit: ");
stop = get_long();
while (start != 0 || stop != 0)
{
if (bad_limits(start, stop, MIN, MAX))
printf("Please try again.\n");
else
{
answer = sum_squares(start, stop);
printf("The sum of the squares of the integers ");
printf("from %ld to %ld is %g\n", start, stop, answer);
}
printf("Enter the limits (enter 0 for both "
"limits to quit):\n");
printf("lower limit: ");
start = get_long();
printf("upper limit: ");
stop = get_long();
}
printf("Done.\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
long get_long(void)
{
long input;
char ch;
//scanf返回正确读入的个数
while (scanf("%ld", &input) != 1)
{
while ((ch = getchar()) != '\n')
putchar(ch); //处理错误输入
printf(" is not an integer.\nPlease enter an");
printf("integer value, such as 25, -178, or 3: ");
}
return input;
}
double sum_squares(long a, long b)
{
double total = 0;
long i;
for (i = a; i <= b; i++)
total += (double)i * (double)i;
return total;
}
bool bad_limits(long begin, long end, long low, long high)
{
bool not_good = false;
if (begin > end)
{
printf("%ld isn't smaller than %ld.\n", begin, end);
not_good = true;
}
if (begin < low || end < low)
{
printf("Values must be %ld or greater.\n", low);
not_good = true;
}
if (begin > high || end > high)
{
printf("Values must be %ld or less.\n", high);
not_good = true;
}
return not_good;
}
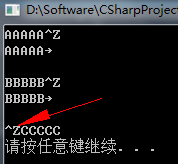
getchar()和putchar()每次只处理一个字符。
示例:获取从键盘输入的字符,并把这些字符发送到屏幕
//Visual Studio中加上这句才可以使用scanf()
//否则只能使用scanf_s()
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
//argc: 参数个数 argv[]: 参数数组
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char ch = 'a';
//循环读取键盘输入的字符,并存入缓冲区
//当按下回车后输出到屏幕
while ((ch = getchar()) != '#')
putchar(ch);//存入缓冲区,按回车后输出到屏幕
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行测试 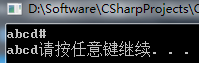
缓冲区
缓冲分两类:
完全缓冲I/O和行缓冲I/O。完全缓冲输入指的是当缓冲区被填满时才刷新缓冲区(内容被发至目的地),通常出现在文件输入中。缓冲区的大小取决于系统,常见的大小是512字节和4096字节。行缓冲I/O指的是在出现换行符时刷新缓冲区。键盘输入通常是行缓冲输入,所以在按下Enter键后才刷新缓冲区。是否能进行无缓冲输入取决于计算机系统。
示例:文件结尾符EOF(End Of File)
//Visual Studio中加上这句才可以使用scanf()
//否则只能使用scanf_s()
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
//argc: 参数个数 argv[]: 参数数组
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
//EOF(End Of File)在stdio.h中被定义#define EOF (-1)
//MS-DOS中会将行首的Ctrl+Z识为结尾符EOF
//UNIX和Linux中,会将行首的Ctrl+D识别为结尾符
//还有一些其他系统会将任意位置的Ctrl+Z识别为结尾符
int ch;
while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF)
{
putchar(ch);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行测试
重定向输入输出
示例:在CMD中运行上例生成的exe文件
< 符号为重定向输入;> 符号为重定向输出
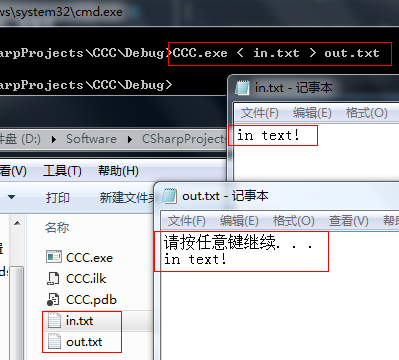
重定向运算符不区别先后,以下两句都是正确的:
CCC.exe < in.txt > out.txt
CCC.exe > out.txt < in.txt
注意: 一些系统要求重定向运算符左侧要有一个空格,右侧没有空格。而其他系统(如,UNIX)允许在重定位运算符两侧有空格或没空格。
示例:输入验证
//Visual Studio中加上这句才可以使用scanf()
//否则只能使用scanf_s()
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// 验证输入是一个整数
long get_long(void);
// 验证范围的上下限是否有效
bool bad_limits(long begin, long end, long low, long high);
// 计算a~b之间的整数平方和
double sum_squares(long a, long b);
//argc: 参数个数 argv[]: 参数数组
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
const long MIN = -10000000L; // 范围的下限
const long MAX = +10000000L; // 范围的上限
long start; // 用户指定的范围最小值
long stop; // 用户指定的范围最大值
double answer;
printf("This program computes the sum of the squares of "
"integers in a range.\nThe lower bound should not "
"be less than -10000000 and \nthe upper bound "
"should not be more than +10000000.\nEnter the "
"limits (enter 0 for both limits to quit):\n"
"lower limit: ");
start = get_long();
printf("upper limit: ");
stop = get_long();
while (start != 0 || stop != 0)
{
if (bad_limits(start, stop, MIN, MAX))
printf("Please try again.\n");
else
{
answer = sum_squares(start, stop);
printf("The sum of the squares of the integers ");
printf("from %ld to %ld is %g\n", start, stop, answer);
}
printf("Enter the limits (enter 0 for both "
"limits to quit):\n");
printf("lower limit: ");
start = get_long();
printf("upper limit: ");
stop = get_long();
}
printf("Done.\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}
long get_long(void)
{
long input;
char ch;
//scanf返回正确读入的个数
while (scanf("%ld", &input) != 1)
{
while ((ch = getchar()) != '\n')
putchar(ch); //处理错误输入
printf(" is not an integer.\nPlease enter an");
printf("integer value, such as 25, -178, or 3: ");
}
return input;
}
double sum_squares(long a, long b)
{
double total = 0;
long i;
for (i = a; i <= b; i++)
total += (double)i * (double)i;
return total;
}
bool bad_limits(long begin, long end, long low, long high)
{
bool not_good = false;
if (begin > end)
{
printf("%ld isn't smaller than %ld.\n", begin, end);
not_good = true;
}
if (begin < low || end < low)
{
printf("Values must be %ld or greater.\n", low);
not_good = true;
}
if (begin > high || end > high)
{
printf("Values must be %ld or less.\n", high);
not_good = true;
}
return not_good;
}
运行测试 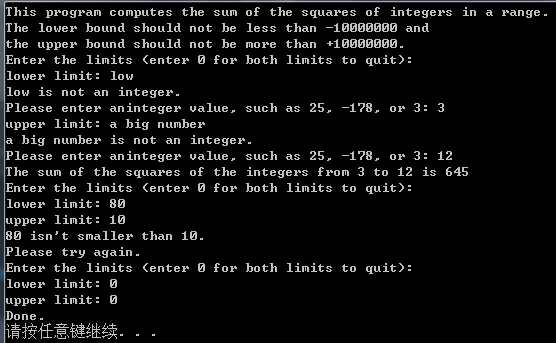
评论:
发表评论: