System.Collections.Generic.List<T>
作者:追风剑情 发布于:2021-1-21 17:38 分类:C#
System.Collections.Generic.List<T>的方法总结
- using System;
- using System.Collections.Generic;
- using System.Linq;
- using System.Text;
- using System.Threading.Tasks;
- namespace ConsoleApp21
- {
- class Program
- {
- static void Main(string[] args)
- {
- int[] intArr = new int[3] { 100, 101, 102 };
- int[] intArrRange = new int[2] { 10, 11 };
- List<int> list = new List<int>();
- list.Capacity = 20;
- list.AddRange(intArr);//添加集合
- for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
- list.Add(i);//添加单个元素
- //在0号位置插入一个元素
- list.Insert(0, 99);
- //在1号位置插入一个集合
- list.InsertRange(1, intArrRange);
- //list能容纳的元素个数(List会自动调整这个大小)
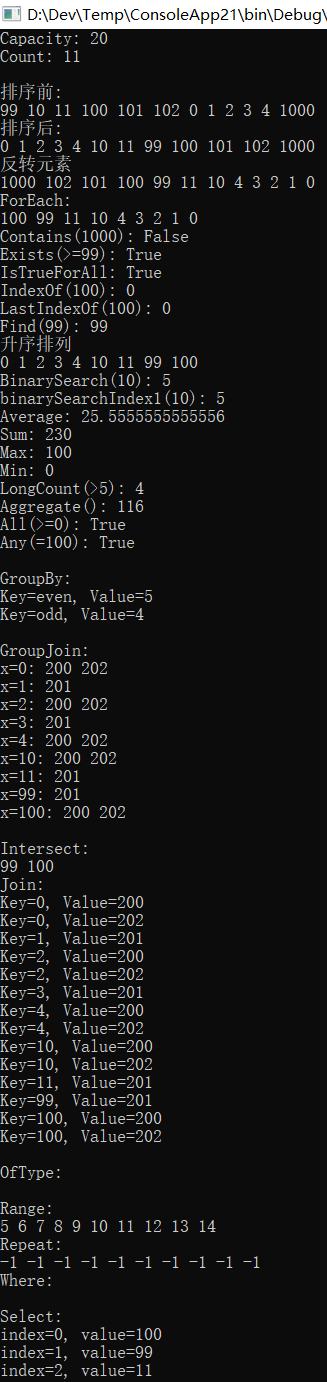
- Console.WriteLine("Capacity: {0}", list.Capacity);
- Console.WriteLine("Count: {0}", list.Count);
- //返回只读集合
- IList<int> readOnlyList = list.AsReadOnly();
- //改变list中的元素会同时影响readOnlyList
- list.Add(1000);
- //获取指定范围的元素
- List<int> range = list.GetRange(1, 5);
- Console.WriteLine("\n排序前:");
- //遍历只读集合
- foreach (int i in readOnlyList)
- Console.Write(i + " ");
- //排序
- list.Sort((a, b) => {
- if (a > b) return 1;
- else if (a == b) return 0;
- return -1;
- });
- Console.WriteLine("\n排序后:");
- //遍历只读集合
- foreach (int i in readOnlyList)
- Console.Write(i + " ");
- Console.WriteLine("\n反转元素");
- //返转所有元素
- list.Reverse();
- //反转指定范围的元素
- //list.Reverse(int index, int count);
- //遍历只读集合
- foreach (int i in readOnlyList)
- Console.Write(i + " ");
- //删除前面两个元素
- list.RemoveRange(0, 2);
- list.Remove(1000);
- list.RemoveAt(0);
- Console.WriteLine("\nForEach:");
- //遍历所有元素
- list.ForEach(delegate(int a)
- {
- Console.Write(a + " ");
- });
- //判断是否包含某个元素
- Console.WriteLine("\nContains(1000): {0}", readOnlyList.Contains(1000));
- //判断是否包含满足某种条件的元素
- Console.WriteLine("Exists(>=99): {0}", list.Exists(x => x >= 99));
- //判断所有元素是否满足某种条件
- bool IsTrueForAll = list.TrueForAll(a=> { return a >= 0; });
- Console.WriteLine("IsTrueForAll: {0}", IsTrueForAll);
- //将列表中的每个元素转成另一种类型
- List<object> objList = list.ConvertAll<object>(new Converter<int, object>(
- input=> { return (object)input; }));
- //注意,无法直接转List
- //List<object> objList = list;
- int[] targetArr = new int[20];
- //将元素复制到目标数组中
- list.CopyTo(targetArr);
- //重载版本
- //list.CopyTo(0, targetArr, 0, list.Count);
- //返回数组
- int[] array = list.ToArray();
- //寻找指定元素所在索引号,未找到返回-1
- int indexOf = list.IndexOf(100);
- int lastIndexOf = list.LastIndexOf(100);
- Console.WriteLine("IndexOf(100): {0}", indexOf);
- Console.WriteLine("LastIndexOf(100): {0}", lastIndexOf);
- //搜索满足条件的第一个元素
- int element = list.Find(x => x == 99);
- Console.WriteLine("Find(99): {0}", element);
- //从后往前搜索
- int elementLast = list.FindLast(x => x == 99);
- //搜索满足条件的所有元素, 以下三种写法等效
- List<int> elements = list.FindAll(x => x == 99);
- //List<int> elements = list.FindAll(x => { return x == 99; });
- //List<int> elements = list.FindAll(delegate (int x) { return x == 99; });
- //搜索满足条件第一个元素的索引号
- int indexFirst = list.FindIndex(x => x == 99);
- //从后往前搜索
- int indexLast = list.FindLastIndex(x => x == 99);
- Console.WriteLine("升序排列");
- list.Sort();
- foreach (int i in list)
- Console.Write(i + " ");
- Console.WriteLine();
- //BinarySearch()适合对已排序的大集合进行搜索
- //使用默认的比较器(Comparer<int>.Default)
- int binarySearchIndex = list.BinarySearch(10);
- //int binarySearchIndex = list.BinarySearch(10, Comparer<int>.Default);
- Console.WriteLine("BinarySearch(10): {0}", binarySearchIndex);
- int binarySearchIndex1 = list.BinarySearch(10, new ListComparer<int>());
- Console.WriteLine("binarySearchIndex1(10): {0}", binarySearchIndex1);
- /*------------- List 扩展方法 -------------*/
- //求平均值
- double average = list.Average();
- //求总和
- int sum = list.Sum();
- //求最大值
- int max = list.Max();
- //求最小值
- int min = list.Min();
- //返回满足条件的元素个数
- long longCount = list.LongCount(x => x > 5);
- int count = list.Count(x => x > 5);
- //累加器,将所有偶数相加
- int aggregate = list.Aggregate(
- (total, next) => next % 2 == 0 ? total + next : total);
- //测试是否所有元素都满足条件
- bool all = list.All(x => x >= 0);
- //测试是否存在满足条件的元素
- bool any = list.Any(x => x == 100);
- Console.WriteLine("Average: {0}", average);
- Console.WriteLine("Sum: {0}", sum);
- Console.WriteLine("Max: {0}", max);
- Console.WriteLine("Min: {0}", min);
- Console.WriteLine("LongCount(>5): {0}", longCount);
- Console.WriteLine("Aggregate(): {0}", aggregate);
- Console.WriteLine("All(>=0): {0}", all);
- Console.WriteLine("Any(=100): {0}", any);
- //追加元素
- //list.Append(5);
- //返回枚举器
- IEnumerable<int> query = list.AsEnumerable();
- //foreach (int i in query)
- // Console.WriteLine(i);
- //强制转换成指定类型,转换失败会抛出InvalidCastException
- IEnumerable<object> cast = list.Cast<object>();
- //连接其他集合
- IEnumerable<int> concat = list.Concat(query);
- //是否包含某个元素
- //list.Contains(100);//使用默认比较器
- //使用自定义比较器
- bool b1 = list.Contains(100, new CustomEqualityComparer());
- //如果list为空,则返回一个带默认值的IEnumerable<>
- IEnumerable<int> enumerable = list.DefaultIfEmpty(0);
- //返回非重复元素集合
- IEnumerable<int> distinct = list.Distinct();//使用默认比较器
- IEnumerable<int> distinct1 = list.Distinct(new CustomEqualityComparer());
- //返回指定位置的元素
- int elementAt = list.ElementAt(0);
- int elementAtOrDefault = list.ElementAtOrDefault(0);//default(TSource)
- //返回一个空集合
- IEnumerable<int> empty = Enumerable.Empty<int>();
- //生成两个集合的差集
- int[] number1 = { 99, 100 };
- //从list中返回不包含number1元素的集合
- IEnumerable<int> except = list.Except(number1);//使用默认比较器
- IEnumerable<int> except1 = list.Except(number1, new CustomEqualityComparer());
- //反回满足条件的第一个元素
- int first = list.First(x => x > 5);
- //int first = list.First();//直接返回第1个元素
- int firstDefault = list.FirstOrDefault(x => x > 5);//default(TSource)
- //int firstDefault = list.FirstOrDefault();
- //返回满足条件的最后一个元素
- //list.Last(x => x > 5);
- //list.Last();
- //list.LastOrDefault(x => x > 5);
- //list.LastOrDefault();
- Console.WriteLine("\nGroupBy:");
- //对集合分组
- var query1 = list.GroupBy(
- //key,这里将元素分为奇数组和偶数组
- x => x % 2 == 0 ? "even" : "odd",
- //对每个元素做处理,这里直接返回x
- x => x,
- //组处理函数(key, 集合)
- (key, intArray) => new
- {
- Key = key,
- Value = intArray.Count() //被分配到key组的元素个数
- });
- foreach(var result in query1)
- {
- Console.WriteLine("Key={0}, Value={1}", result.Key, result.Value);
- }
- Console.WriteLine("\nGroupJoin:");
- //连接分组,以list中的元素为key对join集合元素进行分组
- List<int> join = new List<int>() { 200, 201, 202 };
- var query2 = list.GroupJoin(
- //inner
- join,
- //计算outerKey
- x => x % 2,
- //计算innerKey
- y => y % 2,
- //当innerKey==outerKey时,当前y属性x分组
- (x, yCollection) => new
- {
- Key = x,
- Value = yCollection
- });
- foreach (var result in query2)
- {
- Console.Write("x={0}: ", result.Key);
- foreach (int y in result.Value)
- Console.Write(y + " ");
- Console.WriteLine();
- }
- Console.WriteLine("\nIntersect:");
- //返回两个集合的交集
- List<int> iontersect = new List<int>() { 99, 100, 200 };
- var query3 = list.Intersect(iontersect);
- foreach (int i in query3)
- Console.Write(i + " ");
- Console.WriteLine("\nJoin:");
- var query4 = list.Join(
- //inner
- join,
- //计算outerKey
- x => x % 2,
- //计算innerKey
- y => y % 2,
- //当innerKey==outerKey时,触发此回调
- //即,基于公共键关联两个信息源
- (x, y)=> new {
- Key=x, Value=y
- });
- foreach(var obj in query4)
- {
- Console.WriteLine("Key={0}, Value={1}", obj.Key, obj.Value);
- }
- Console.WriteLine("\nOfType:");
- //从集合中筛选出指定类型的元素
- var query5 = list.OfType<int>();
- //对元素按升序排序
- IEnumerable<int> query6 = list.OrderBy(x=>x);
- //对元素按降序排序
- IEnumerable<int> query7 = list.OrderByDescending(x => x);
- //在列表的开头添加元素
- //list.Prepend(0);
- Console.WriteLine("\nRange:");
- //从5开始生成10个元素
- IEnumerable<int> range1 = Enumerable.Range(5, 10);
- foreach (int i in range1)
- Console.Write(i+" ");
- Console.WriteLine("\nRepeat:");
- //生成10个值为-1的元素
- IEnumerable<int> range2 = Enumerable.Repeat(-1, 10);
- foreach (int i in range2)
- Console.Write(i + " ");
- Console.WriteLine("\nWhere:");
- //返回满足条件的集合
- IEnumerable<int> query8 = list.Where(x=>x>50);
- //反转元素顺序
- list.Reverse();
- Console.WriteLine("\nSelect:");
- //将所有元素投影到新集合中
- var select = list.Select((x, index) => new {
- index = index,
- value = x
- });
- foreach (var obj in select)
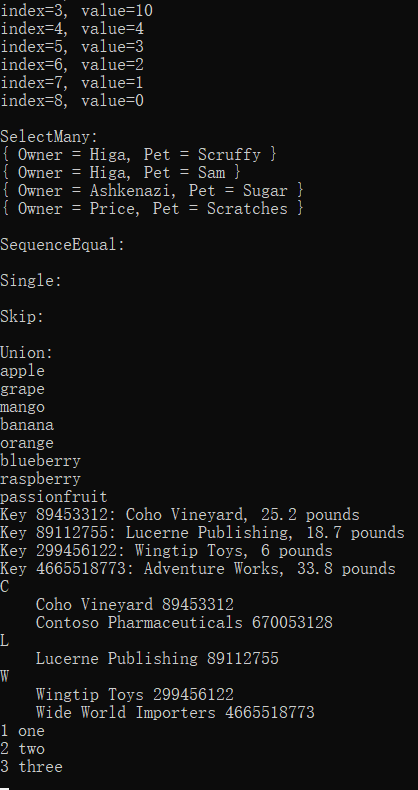
- Console.WriteLine("index={0}, value={1}", obj.index, obj.value);
- Console.WriteLine("\nSelectMany:");
- SelectManyEx3();
- Console.WriteLine("\nSequenceEqual:");
- //比较两个集合是否相等
- List<int> equal = new List<int>() { 1,2 };
- bool b2 = list.SequenceEqual(equal);//使用默认比较器
- Console.WriteLine("\nSingle:");
- //返回序列中满足指定条件的唯一元素;如果有多个这样的元素存在,则会引发异常。
- int element1 = list.Single(x=>x<1);
- int element2 = list.SingleOrDefault(x=>x<0);
- Console.WriteLine("\nSkip:");
- //跳过前3个元素,返回一个新集合
- IEnumerable<int> query9 = list.Skip(3);
- //省略后3个元素,返回一个新集合
- //IEnumerable<int> query10 = list.SkipLast(3);
- //返回条件判断为false的元素
- IEnumerable<int> query11 = list.SkipWhile(x => x >= 80);
- //返回前3个元素
- IEnumerable<int> query12 = list.Take(3);
- //返回后3个元素
- //IEnumerable<int> query13 = list.TakeLast(3);
- //返回条件判断为true的元素
- IEnumerable<int> query13 = list.TakeWhile(x=>x>80);
- //list.ToHashSet();
- List<int> list1 = list.ToList();
- Console.WriteLine("\nUnion:");
- //返回非重复元素的并集
- List<int> union = new List<int>() { 1,2,400};
- IEnumerable<int> query14 = list.Union(union);
- TakeByEx();
- ToDictionaryEx1();
- ToLookupEx1();
- ZipEx();
- //仅保留元素实际所占用的内存空间
- list.TrimExcess();
- //清空列表
- list.Clear();
- Console.ReadLine();
- }
- //官方示例
- public static void SelectManyEx3()
- {
- PetOwner[] petOwners = {
- new PetOwner { Name="Higa",
- Pets = new List<string>{ "Scruffy", "Sam" } },
- new PetOwner { Name="Ashkenazi",
- Pets = new List<string>{ "Walker", "Sugar" } },
- new PetOwner { Name="Price",
- Pets = new List<string>{ "Scratches", "Diesel" } },
- new PetOwner { Name="Hines",
- Pets = new List<string>{ "Dusty" } } };
- // Project the pet owner's name and the pet's name.
- var query = petOwners.SelectMany(
- //理解成一级遍历
- //遍历集合中的每个元素
- petOwner => petOwner.Pets,
- //理解成二级遍历
- //遍历Pets集合 (petName是Pets中的元素)
- (petOwner, petName) => new { petOwner, petName })
- //End SelectMany
- //-- 继续筛选 --
- //返回以S开头的宠物名称集合
- .Where(ownerAndPet => ownerAndPet.petName.StartsWith("S"))
- //返回一个新集合
- .Select(ownerAndPet =>
- new
- {
- Owner = ownerAndPet.petOwner.Name,
- Pet = ownerAndPet.petName
- }
- );
- // Print the results.
- foreach (var obj in query)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(obj);
- }
- }
- //官方示例
- public static void TakeByEx()
- {
- string[] fruits = { "grape", "passionfruit", "banana", "mango",
- "orange", "raspberry", "apple", "blueberry" };
- // Sort the strings first by their length and then
- //alphabetically by passing the identity selector function.
- //OrderBy为一级排序,ThenBy在一级排序的基础上排序
- IEnumerable<string> query =
- fruits.OrderBy(fruit => fruit.Length).ThenBy(fruit => fruit);
- /*
- IEnumerable<string> query1 =
- fruits
- .OrderBy(fruit => fruit.Length)
- //降序排序
- .ThenByDescending(fruit => fruit);
- */
- foreach (string fruit in query)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(fruit);
- }
- /*
- This code produces the following output:
- apple
- grape
- mango
- banana
- orange
- blueberry
- raspberry
- passionfruit
- */
- }
- //List转Dictionary
- public static void ToDictionaryEx1()
- {
- List<Package> packages =
- new List<Package>
- { new Package { Company = "Coho Vineyard", Weight = 25.2, TrackingNumber = 89453312L },
- new Package { Company = "Lucerne Publishing", Weight = 18.7, TrackingNumber = 89112755L },
- new Package { Company = "Wingtip Toys", Weight = 6.0, TrackingNumber = 299456122L },
- new Package { Company = "Adventure Works", Weight = 33.8, TrackingNumber = 4665518773L } };
- // Create a Dictionary of Package objects,
- // using TrackingNumber as the key.
- Dictionary<long, Package> dictionary =
- packages.ToDictionary(p => p.TrackingNumber);
- foreach (KeyValuePair<long, Package> kvp in dictionary)
- {
- Console.WriteLine(
- "Key {0}: {1}, {2} pounds",
- kvp.Key,
- kvp.Value.Company,
- kvp.Value.Weight);
- }
- }
- //List转查找表(Lookup)
- public static void ToLookupEx1()
- {
- // Create a list of Packages.
- List<Package> packages =
- new List<Package>
- { new Package { Company = "Coho Vineyard",
- Weight = 25.2, TrackingNumber = 89453312L },
- new Package { Company = "Lucerne Publishing",
- Weight = 18.7, TrackingNumber = 89112755L },
- new Package { Company = "Wingtip Toys",
- Weight = 6.0, TrackingNumber = 299456122L },
- new Package { Company = "Contoso Pharmaceuticals",
- Weight = 9.3, TrackingNumber = 670053128L },
- new Package { Company = "Wide World Importers",
- Weight = 33.8, TrackingNumber = 4665518773L } };
- // Create a Lookup to organize the packages.
- // Use the first character of Company as the key value.
- // Select Company appended to TrackingNumber
- // as the element values of the Lookup.
- ILookup<char, string> lookup =
- packages
- .ToLookup(p => Convert.ToChar(p.Company.Substring(0, 1)),
- p => p.Company + " " + p.TrackingNumber);
- // Iterate through each IGrouping in the Lookup.
- foreach (IGrouping<char, string> packageGroup in lookup)
- {
- // Print the key value of the IGrouping.
- Console.WriteLine(packageGroup.Key);
- // Iterate through each value in the
- // IGrouping and print its value.
- foreach (string str in packageGroup)
- Console.WriteLine(" {0}", str);
- }
- }
- //合并两个序列
- public static void ZipEx()
- {
- int[] numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
- string[] words = { "one", "two", "three" };
- var numbersAndWords = numbers.Zip(words, (first, second) => first + " " + second);
- foreach (var item in numbersAndWords)
- Console.WriteLine(item);
- }
- }
- //自定义二叉搜索比较器
- public class ListComparer<T> : IComparer<T> where T : IComparable
- {
- //这里的比较方式要与List中的元素排序方式一致
- //例如:List中的元素是升序的,这里的判断也必须是升序的
- public int Compare(T x, T y)
- {
- if (x == null)
- return y != null ? -1 : 0;
- if (y == null)
- return 1;
- if (x is T && y is T)
- return x.CompareTo(y);
- return 0;
- }
- }
- //自定义相等比较器
- class CustomEqualityComparer : IEqualityComparer<int>
- {
- public bool Equals(int x, int y)
- {
- return x == y;
- }
- public int GetHashCode(int obj)
- {
- return obj.GetHashCode();
- }
- }
- class PetOwner
- {
- public string Name { get; set; }
- public List<string> Pets { get; set; }
- }
- class Package
- {
- public string Company { get; set; }
- public double Weight { get; set; }
- public long TrackingNumber { get; set; }
- }
- }
标签: C#
日历
最新文章
随机文章
热门文章
分类
存档
- 2025年3月(4)
- 2025年2月(3)
- 2025年1月(1)
- 2024年12月(5)
- 2024年11月(5)
- 2024年10月(5)
- 2024年9月(3)
- 2024年8月(3)
- 2024年7月(11)
- 2024年6月(3)
- 2024年5月(9)
- 2024年4月(10)
- 2024年3月(11)
- 2024年2月(24)
- 2024年1月(12)
- 2023年12月(3)
- 2023年11月(9)
- 2023年10月(7)
- 2023年9月(2)
- 2023年8月(7)
- 2023年7月(9)
- 2023年6月(6)
- 2023年5月(7)
- 2023年4月(11)
- 2023年3月(6)
- 2023年2月(11)
- 2023年1月(8)
- 2022年12月(2)
- 2022年11月(4)
- 2022年10月(10)
- 2022年9月(2)
- 2022年8月(13)
- 2022年7月(7)
- 2022年6月(11)
- 2022年5月(18)
- 2022年4月(29)
- 2022年3月(5)
- 2022年2月(6)
- 2022年1月(8)
- 2021年12月(5)
- 2021年11月(3)
- 2021年10月(4)
- 2021年9月(9)
- 2021年8月(14)
- 2021年7月(8)
- 2021年6月(5)
- 2021年5月(2)
- 2021年4月(3)
- 2021年3月(7)
- 2021年2月(2)
- 2021年1月(8)
- 2020年12月(7)
- 2020年11月(2)
- 2020年10月(6)
- 2020年9月(9)
- 2020年8月(10)
- 2020年7月(9)
- 2020年6月(18)
- 2020年5月(4)
- 2020年4月(25)
- 2020年3月(38)
- 2020年1月(21)
- 2019年12月(13)
- 2019年11月(29)
- 2019年10月(44)
- 2019年9月(17)
- 2019年8月(18)
- 2019年7月(25)
- 2019年6月(25)
- 2019年5月(17)
- 2019年4月(10)
- 2019年3月(36)
- 2019年2月(35)
- 2019年1月(28)
- 2018年12月(30)
- 2018年11月(22)
- 2018年10月(4)
- 2018年9月(7)
- 2018年8月(13)
- 2018年7月(13)
- 2018年6月(6)
- 2018年5月(5)
- 2018年4月(13)
- 2018年3月(5)
- 2018年2月(3)
- 2018年1月(8)
- 2017年12月(35)
- 2017年11月(17)
- 2017年10月(16)
- 2017年9月(17)
- 2017年8月(20)
- 2017年7月(34)
- 2017年6月(17)
- 2017年5月(15)
- 2017年4月(32)
- 2017年3月(8)
- 2017年2月(2)
- 2017年1月(5)
- 2016年12月(14)
- 2016年11月(26)
- 2016年10月(12)
- 2016年9月(25)
- 2016年8月(32)
- 2016年7月(14)
- 2016年6月(21)
- 2016年5月(17)
- 2016年4月(13)
- 2016年3月(8)
- 2016年2月(8)
- 2016年1月(18)
- 2015年12月(13)
- 2015年11月(15)
- 2015年10月(12)
- 2015年9月(18)
- 2015年8月(21)
- 2015年7月(35)
- 2015年6月(13)
- 2015年5月(9)
- 2015年4月(4)
- 2015年3月(5)
- 2015年2月(4)
- 2015年1月(13)
- 2014年12月(7)
- 2014年11月(5)
- 2014年10月(4)
- 2014年9月(8)
- 2014年8月(16)
- 2014年7月(26)
- 2014年6月(22)
- 2014年5月(28)
- 2014年4月(15)
友情链接
- Unity官网
- Unity圣典
- Unity在线手册
- Unity中文手册(圣典)
- Unity官方中文论坛
- Unity游戏蛮牛用户文档
- Unity下载存档
- Unity引擎源码下载
- Unity服务
- Unity Ads
- wiki.unity3d
- Visual Studio Code官网
- SenseAR开发文档
- MSDN
- C# 参考
- C# 编程指南
- .NET Framework类库
- .NET 文档
- .NET 开发
- WPF官方文档
- uLua
- xLua
- SharpZipLib
- Protobuf-net
- Protobuf.js
- OpenSSL
- OPEN CASCADE
- JSON
- MessagePack
- C在线工具
- 游戏蛮牛
- GreenVPN
- 聚合数据
- 热云
- 融云
- 腾讯云
- 腾讯开放平台
- 腾讯游戏服务
- 腾讯游戏开发者平台
- 腾讯课堂
- 微信开放平台
- 腾讯实时音视频
- 腾讯即时通信IM
- 微信公众平台技术文档
- 白鹭引擎官网
- 白鹭引擎开放平台
- 白鹭引擎开发文档
- FairyGUI编辑器
- PureMVC-TypeScript
- 讯飞开放平台
- 亲加通讯云
- Cygwin
- Mono开发者联盟
- Scut游戏服务器引擎
- KBEngine游戏服务器引擎
- Photon游戏服务器引擎
- 码云
- SharpSvn
- 腾讯bugly
- 4399原创平台
- 开源中国
- Firebase
- Firebase-Admob-Unity
- google-services-unity
- Firebase SDK for Unity
- Google-Firebase-SDK
- AppsFlyer SDK
- android-repository
- CQASO
- Facebook开发者平台
- gradle下载
- GradleBuildTool下载
- Android Developers
- Google中国开发者
- AndroidDevTools
- Android社区
- Android开发工具
- Google Play Games Services
- Google商店
- Google APIs for Android
- 金钱豹VPN
- TouchSense SDK
- MakeHuman
- Online RSA Key Converter
- Windows UWP应用
- Visual Studio For Unity
- Open CASCADE Technology
- 慕课网
- 阿里云服务器ECS
- 在线免费文字转语音系统
- AI Studio
- 网云穿
- 百度网盘开放平台
- 迅捷画图
- 菜鸟工具
- [CSDN] 程序员研修院
- 华为人脸识别
- 百度AR导航导览SDK
- 海康威视官网
- 海康开放平台
- 海康SDK下载
- git download
- Open CASCADE
- CascadeStudio
交流QQ群
-
Flash游戏设计: 86184192
Unity游戏设计: 171855449
游戏设计订阅号