动态分配内存malloc()和free()
作者:追风剑情 发布于:2019-11-25 19:41 分类:C
示例
- //Visual Studio中加上这句才可以使用scanf()
- //否则只能使用scanf_s()
- #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #include <ctype.h>
- //malloc()、free()
- #include <stdlib.h>
- //argc: 参数个数 argv[]: 参数数组
- //int main(int argc, char **argv)
- int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- double * ptd;
- int max;
- int number;
- int i = 0;
- puts("What is the maximum number of type double entries?");
- if (scanf("%d", &max) != 1)
- {
- puts("Number not correctly entered -- bye.");
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE);//程序异常中止
- }
- //动态分配内存
- /*在C中,不一定要使用强制类型转换(double *),但是在C++中必须使用。
- 所以,使用强制类型转换更容易把C程序转换为C++程序。*/
- ptd = (double *)malloc(max * sizeof(double));
- if (ptd == NULL)
- {
- puts("Memory allocation failed. Goodbye.");
- exit(EXIT_FAILURE);//程序异常中止
- }
- //EXIT_FAILURE表示异常中止
- //EXIT_SUCCESS表示程序正常结束
- //一些操作系统(包括UNIX、Linux和Windows)还接受一些表示
- //其他运行错误的整数值.
- /* ptd现在指向有max个元素的数组 */
- puts("Enter the values (q to quit):");
- while (i < max && scanf("%lf", &ptd[i]) == 1)
- ++i;
- printf("Here are your %d entries:\n", number = i);
- for (i = 0; i < number; i++)
- {
- printf("%7.2f ", ptd[i]);
- if (i % 7 == 6)
- putchar('\n');
- }
- if (i % 7 != 0)
- putchar('\n');
- puts("Done.");
- //释放动态分配的内存
- /*free()函数释放由malloc()分配的内存。free()只释放其参数指向的内存块。
- 一些操作系统在程序结束时会自动释放动态分配的内存,但是有些系统不会。
- 为保险起见,请使用free(),不要依赖操作系统来清理。
- 不能用free()释放通过其他方式(如,声明一个数组)分配的内存。*/
- free(ptd);
- system("pause");
- return 0;
- }
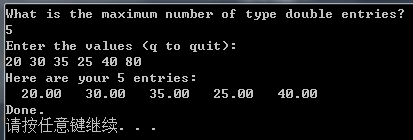
运行测试
标签: C语言
日历
最新文章
随机文章
热门文章
分类
存档
- 2025年3月(4)
- 2025年2月(3)
- 2025年1月(1)
- 2024年12月(5)
- 2024年11月(5)
- 2024年10月(5)
- 2024年9月(3)
- 2024年8月(3)
- 2024年7月(11)
- 2024年6月(3)
- 2024年5月(9)
- 2024年4月(10)
- 2024年3月(11)
- 2024年2月(24)
- 2024年1月(12)
- 2023年12月(3)
- 2023年11月(9)
- 2023年10月(7)
- 2023年9月(2)
- 2023年8月(7)
- 2023年7月(9)
- 2023年6月(6)
- 2023年5月(7)
- 2023年4月(11)
- 2023年3月(6)
- 2023年2月(11)
- 2023年1月(8)
- 2022年12月(2)
- 2022年11月(4)
- 2022年10月(10)
- 2022年9月(2)
- 2022年8月(13)
- 2022年7月(7)
- 2022年6月(11)
- 2022年5月(18)
- 2022年4月(29)
- 2022年3月(5)
- 2022年2月(6)
- 2022年1月(8)
- 2021年12月(5)
- 2021年11月(3)
- 2021年10月(4)
- 2021年9月(9)
- 2021年8月(14)
- 2021年7月(8)
- 2021年6月(5)
- 2021年5月(2)
- 2021年4月(3)
- 2021年3月(7)
- 2021年2月(2)
- 2021年1月(8)
- 2020年12月(7)
- 2020年11月(2)
- 2020年10月(6)
- 2020年9月(9)
- 2020年8月(10)
- 2020年7月(9)
- 2020年6月(18)
- 2020年5月(4)
- 2020年4月(25)
- 2020年3月(38)
- 2020年1月(21)
- 2019年12月(13)
- 2019年11月(29)
- 2019年10月(44)
- 2019年9月(17)
- 2019年8月(18)
- 2019年7月(25)
- 2019年6月(25)
- 2019年5月(17)
- 2019年4月(10)
- 2019年3月(36)
- 2019年2月(35)
- 2019年1月(28)
- 2018年12月(30)
- 2018年11月(22)
- 2018年10月(4)
- 2018年9月(7)
- 2018年8月(13)
- 2018年7月(13)
- 2018年6月(6)
- 2018年5月(5)
- 2018年4月(13)
- 2018年3月(5)
- 2018年2月(3)
- 2018年1月(8)
- 2017年12月(35)
- 2017年11月(17)
- 2017年10月(16)
- 2017年9月(17)
- 2017年8月(20)
- 2017年7月(34)
- 2017年6月(17)
- 2017年5月(15)
- 2017年4月(32)
- 2017年3月(8)
- 2017年2月(2)
- 2017年1月(5)
- 2016年12月(14)
- 2016年11月(26)
- 2016年10月(12)
- 2016年9月(25)
- 2016年8月(32)
- 2016年7月(14)
- 2016年6月(21)
- 2016年5月(17)
- 2016年4月(13)
- 2016年3月(8)
- 2016年2月(8)
- 2016年1月(18)
- 2015年12月(13)
- 2015年11月(15)
- 2015年10月(12)
- 2015年9月(18)
- 2015年8月(21)
- 2015年7月(35)
- 2015年6月(13)
- 2015年5月(9)
- 2015年4月(4)
- 2015年3月(5)
- 2015年2月(4)
- 2015年1月(13)
- 2014年12月(7)
- 2014年11月(5)
- 2014年10月(4)
- 2014年9月(8)
- 2014年8月(16)
- 2014年7月(26)
- 2014年6月(22)
- 2014年5月(28)
- 2014年4月(15)
友情链接
- Unity官网
- Unity圣典
- Unity在线手册
- Unity中文手册(圣典)
- Unity官方中文论坛
- Unity游戏蛮牛用户文档
- Unity下载存档
- Unity引擎源码下载
- Unity服务
- Unity Ads
- wiki.unity3d
- Visual Studio Code官网
- SenseAR开发文档
- MSDN
- C# 参考
- C# 编程指南
- .NET Framework类库
- .NET 文档
- .NET 开发
- WPF官方文档
- uLua
- xLua
- SharpZipLib
- Protobuf-net
- Protobuf.js
- OpenSSL
- OPEN CASCADE
- JSON
- MessagePack
- C在线工具
- 游戏蛮牛
- GreenVPN
- 聚合数据
- 热云
- 融云
- 腾讯云
- 腾讯开放平台
- 腾讯游戏服务
- 腾讯游戏开发者平台
- 腾讯课堂
- 微信开放平台
- 腾讯实时音视频
- 腾讯即时通信IM
- 微信公众平台技术文档
- 白鹭引擎官网
- 白鹭引擎开放平台
- 白鹭引擎开发文档
- FairyGUI编辑器
- PureMVC-TypeScript
- 讯飞开放平台
- 亲加通讯云
- Cygwin
- Mono开发者联盟
- Scut游戏服务器引擎
- KBEngine游戏服务器引擎
- Photon游戏服务器引擎
- 码云
- SharpSvn
- 腾讯bugly
- 4399原创平台
- 开源中国
- Firebase
- Firebase-Admob-Unity
- google-services-unity
- Firebase SDK for Unity
- Google-Firebase-SDK
- AppsFlyer SDK
- android-repository
- CQASO
- Facebook开发者平台
- gradle下载
- GradleBuildTool下载
- Android Developers
- Google中国开发者
- AndroidDevTools
- Android社区
- Android开发工具
- Google Play Games Services
- Google商店
- Google APIs for Android
- 金钱豹VPN
- TouchSense SDK
- MakeHuman
- Online RSA Key Converter
- Windows UWP应用
- Visual Studio For Unity
- Open CASCADE Technology
- 慕课网
- 阿里云服务器ECS
- 在线免费文字转语音系统
- AI Studio
- 网云穿
- 百度网盘开放平台
- 迅捷画图
- 菜鸟工具
- [CSDN] 程序员研修院
- 华为人脸识别
- 百度AR导航导览SDK
- 海康威视官网
- 海康开放平台
- 海康SDK下载
- git download
- Open CASCADE
- CascadeStudio
交流QQ群
-
Flash游戏设计: 86184192
Unity游戏设计: 171855449
游戏设计订阅号